Get Easy Health Digest™ in your inbox and don’t miss a thing when you subscribe today. Plus, get the free bonus report, Mother Nature’s Tips, Tricks and Remedies for Cholesterol, Blood Pressure & Blood Sugar as my way of saying welcome to the community!
Give your body an oil change for better health

Polyunsaturated fats (aka vegetable oils) have long been accepted as the best fats for your health.
After all, they provide heart-healthy benefits, and mainstream medicine likes to claim they’ll save you from the “dangers of high cholesterol”… though we now know their cholesterol connection to heart disease was based on flawed studies.
In fact, cholesterol is brain fuel and you should be more concerned with balancing it than blindly lowering it…
Balancing fats is just as important. And there are two very important essential fatty acids that most of us are completely off balance with… and the problem stems from the vegetable oil in your kitchen.
As it turns out, not all vegetable oils are created equal. So, it might be time to give your body an “oil change.” Because rather than supporting your health pursuits, some vegetable oils could be preventing your progress… or even worse, leading to disease.
The truth about polyunsaturated fats revealed
There are two types of polyunsaturated fats:
- Omega-6
- Omega-3
These are both essential fats — essential meaning your body can’t produce them internally so you need to consume them in your diet. Though these are lumped under the same health-promoting umbrella, they are very, very different fats.
Quite simply:
- Omega-6 fats are pro-inflammatory.
- Omega-3 fats are anti-inflammatory.
While your body does need both of these fats, the ratio of omega-6s to omega-3s in your body is meant to be around 2:1 or a maximum of 4:1. The major problem with the modern Western diet is you’re likely consuming far too many omega 6 fats. As a consequence, studies show the omega 6/3 ratio can climb as high as 20:1.
But what if you’re a regular reader of Easy Health Options, and you’ve headed the expert nutritional advice of contributors like me or Virginia Tims-Lawson by supplementing with a high-quality omega-3 fish oil supplement?
Would that mean that despite following the Western diet, you have a higher ratio of healthy omega-3s circulating in your body versus the not-so-healthy omega-6s?
Unfortunately, no…
Because both omega-6s and omega-3s compete for the same conversion enzymes in your body, excessive consumption of omega 6s significantly decreases the conversion of your omega-3s. And that’s a real concern…
Common omega-6-related health problems
Research clearly shows that omega-6 fats increase inflammation in the body’s cells — they are proinflammatory — and chronic inflammation in your cells leads to all types of diseases.
Excessive omega-6 has been linked to:
- Atherosclerosis
- Asthma
- Arthritis
- Bone loss
- Cancer
- Heart attacks
- Depression
- Behavioral problems
- Migraine
Omega-6 and Omega-3 in cooking oils and food sources
All those vegetable oils you thought were so heart-healthy — corn, cottonseed, soybean, grape seed, sunflower — are in fact the opposite. They are high in omega-6 fats and therefore, increasing inflammation in your body.
Here’s a chart showing the fat ratios in different sources.
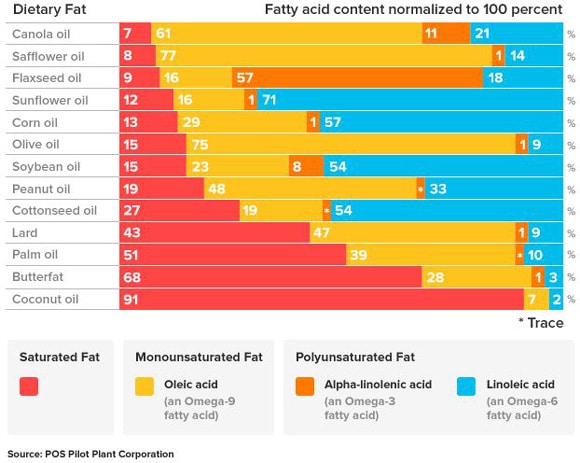
And here you can get a better picture of omega-6s and omega-3s in foods:
| Foods high in omega 6 | Foods high in omega 3 |
| Vegetable oils – sunflower, soybean, cottonseed, peanut, corn, grape seed
Margarines Grains Conventional meats Sunflower seeds, pine nuts, butternuts |
Salmon
Sardines Mackerel Flaxseed Chia seeds Hemp seed |
On top of this, in a modern Western diet, high consumption of grain-based foods in the form of processed and packaged foods is now common practice. These same foods often contain low quality vegetable oils, so together these contribute to your omega-6 inflammatory load.
And if you’re wondering how conventional meats get on the list, animals are fed grains so as a consequence, meat tends to be higher in omega 6 fats. Grass fed and organic raised animals on the other hand, contain higher omega 3 fat content.
10 practical steps to give your body an oil change
The good news is, studies show that decreasing your intake of omega-6 fats and increasing intake of omega-3s provides strong medicinal and protective health benefits.
Follow these simple steps to give yourself an oil change:
- Purchase organic free range meats and poultry as a first option
- Choose grass fed beef instead of conventional beef
- Eat free range eggs
- Limit grain intake to one cup a day maximum
- Reduce or eliminate processed and packaged food items
- Use virgin olive oil or coconut oil in place of other vegetable oils
- Eat more vegetables in place of your grains
- Eat fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, tuna, mackerel, herring, on a weekly basis
- Consume seeds – hemp, flax and chia on a daily basis
- Take an omega 3 fish oil or flaxseed oil supplement
Sources:
-
Lands B, et al. Dynamic interactions of n-3 and n-6 fatty acid nutrients. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2017;S0952-3278(16):30152-1
-
Bibus D, et al. Balancing proportions of competing omega-3 and omega-6 highly unsaturated fatty acids (HUFA) in tissue lipids. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2015;99:19-23.
-
Kresser K. Retrieved February 21, 2017, from https://chriskresser.com/how-too-much-omega-6-and-not-enough-omega-3-is-making-us-sick/












