Get Easy Health Digest™ in your inbox and don’t miss a thing when you subscribe today. Plus, get the free bonus report, Mother Nature’s Tips, Tricks and Remedies for Cholesterol, Blood Pressure & Blood Sugar as my way of saying welcome to the community!
5 health issues that cause muscle cramps
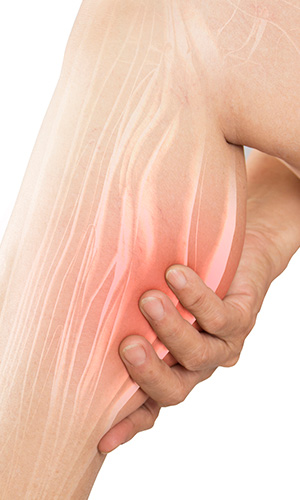
Muscle cramps are sudden, involuntary muscle contractions that can be triggered by electrolyte imbalance, dehydration, nerve signaling issues and underlying health conditions. Research suggests that nutrient status, hydration, and neuromuscular function all play a role in cramp frequency and severity.
But no matter what’s causing your muscle cramps, regular cramping isn’t something you should ignore. It’s your body’s way of telling you something’s not right.
If you pay attention to the signs, you can most likely narrow it down to one of six common causes of cramping and know if it’s necessary to seek care:

1. The impact of overworked muscles in muscle cramps
If you’re exercising extra hard, you could end up with muscle cramps. These types of muscle cramps are pretty easy to spot because they usually happen after a vigorous workout. The best way to prevent cramps from overworked muscles is to scale back your exercise routine and make sure to stretch before you work out.

2. The role of electrolyte imbalance in muscle cramps
When people are active in the heat, run long distances, or work out in elevated temperatures, or for extended periods, they lose electrolytes and fluids through sweating. As a result, dehydration and electrolyte imbalances can trigger muscle spasms and cramps. While active, keep water or electrolyte replacement drinks nearby and remember to stop and drink.

3. The role of compressed nerves in muscle cramps
If the nerves in your spine are compressed, you can experience cramps in your legs. You can tell if this is the cause of cramping because the pain gets worse the longer you walk. The pain should also improve a bit if you walk with your back slightly flexed, as you would when pushing a shopping cart.

4. The role of poor blood circulation in muscle cramps
If your legs aren’t getting enough blood, you’ll likely experience some painful cramping. If poor blood circulation is the cause of your cramping, you’ll feel more pain while you’re exercising. When you stop exercising, the cramps should get better.
5. The role of a mineral deficiency in muscle cramps
Mineral deficiencies could be the culprit of muscle cramps that occur without an apparent cause. Some mineral deficiencies that can contribute to muscle cramps include potassium, calcium, and magnesium deficiencies. If you suspect one of these deficiencies is at the root of your constant cramping, ask your physician about performing a blood test to know for sure.

Nutrients most commonly linked to muscle function
Magnesium: Vital for regulating muscle and nerve function.
Potassium: Works with sodium to enable muscle contractions.
Calcium: Essential for muscles to lengthen or shorten properly during movement.
Sodium: Crucial to manage fluid balance.
Vitamin D: A must for calcium absorption.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine): For nerve health and energy production.
When muscle cramps may signal medical issues
Muscle cramps resulting from activity are normal and should be short-lived. However, severe, frequent, and long-lasting muscle cramps are concerning and warrant a visit to a doctor. If muscle cramps are accompanied by swelling, redness, warmth, muscle weakness or numbness, seek care immediately.
Sources:
- Muscle Cramp — The Mayo Clinic
Editor’s note: Did you know that when you take your body from acid to alkaline you can boost your energy, lose weight, soothe digestion, avoid illness and achieve wellness? Click here to discover The Alkaline Secret to Ultimate Vitality and revive your life today!


















